
The strength of our approach was to combine behavioral analyses and in vivo imaging of brain activities in the same animals. To solve those challenges, says Löwel, we didnt need to develop totally new techniques, but used well-establish ways of answering a question that is very often addressed using only in vitro techniques.
Witte, and Klaus Kreikemeier, the primary challenges facing the research team were selecting the lesion model that best addressed their questions, as well as controlling reproducible lesion size and location. Siegrid Löwels Systems Neuroscience Group, along with Silvio Schmidt, Karl-Friedrich Schmidt, Otto W.
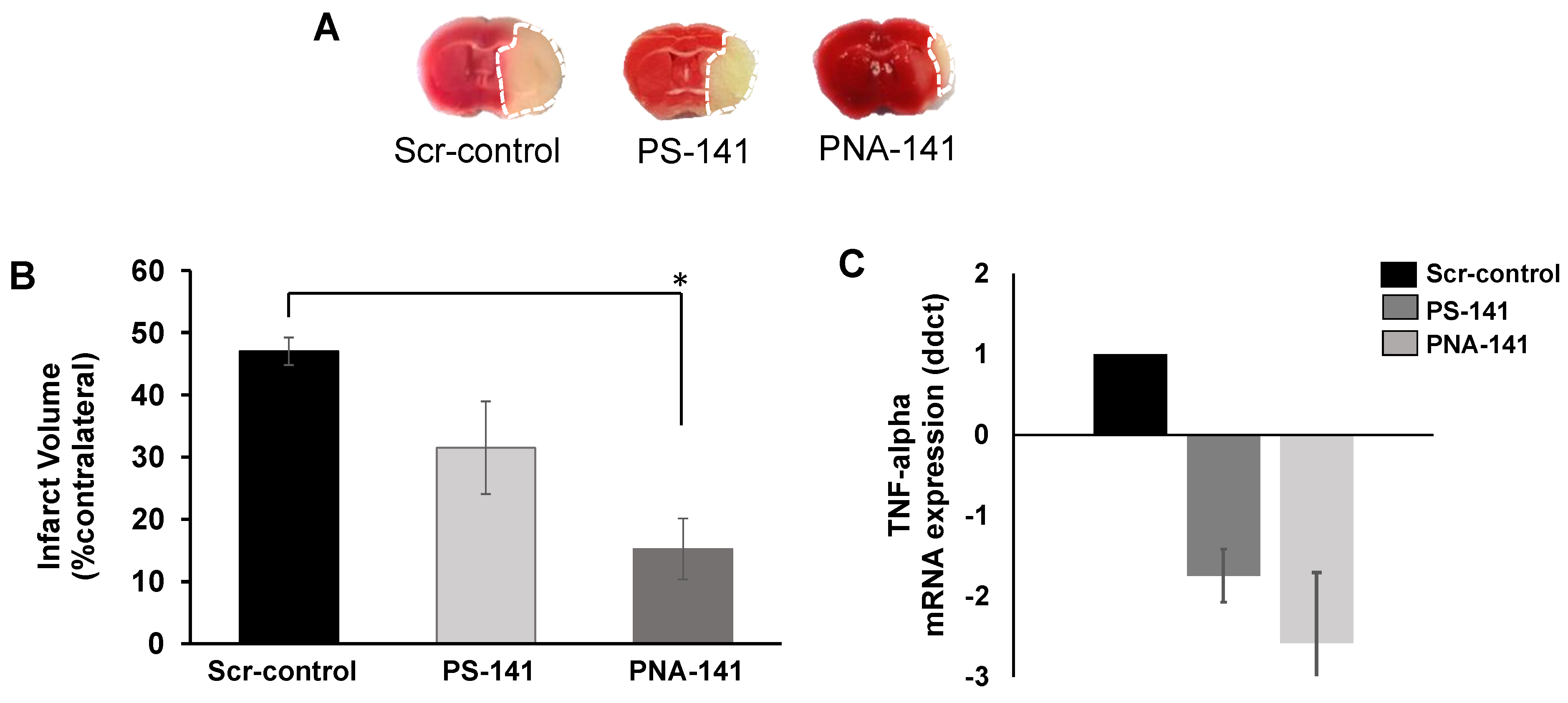
Moreover, in a finding significant to researchers modeling the visual system, the study clearly demonstrates that nonlocal influences i.e., factors outside of the visual cortex or visual system can modify the sensitivity of the visual cortex to changes in afferent activity patterns and are thus more important in OD-plasticity than has previously been thought.Ĭonducted by Franziska Greifzu, a graduate student in Prof. The researchers were thus able to conclude that both sensory learning and OD-plasticity are compromised in the areas surrounding a cortical lesion, and that transient inflammation is responsible for impaired sensory learning suggesting that anti-inflammatory treatment may be useful adjuvant therapy in post-stroke rehabilitation. In addition, anti-inflammatory treatment restored sensory learning but not OD-plasticity the same results obtained by implementing a two-week delay between photothrombosis and MD. Recently, however, research conducted at the Bernstein Fokus Neurotechnologie (BFNT) and Johann-Friedrich-Blumenbach Institut für Zoologie und Anthropologie at Universität Göttingen in Germany has shown that after a photothrombotically-induced stroke outside the visual system (a lesion induced in the mouse somatosensory cortex by intravenous injection of photosensitive dyes that, when irradiated, cause photochemical occlusion of the irradiated vessels with secondary tissue ischemia), there was neither an enhancement of visual acuity nor an OD-shift after MD but OD-plasticity was present in the hemisphere contralateral to the lesion.

A standard view holds that changes in the activity of the major thalamocortical afferents to the visual cortex (the afferents from the left and right eye) are sufficient to induce OD-plasticity. (Medical Xpress) - One of the many potential consequences of ischemic stroke a lesion, or localized pathological change in the brain, in which blood flow insufficient to meet metabolic demand leads to poor oxygen supply ( cerebral hypoxia) is compromise to two different visual plasticity paradigms: sensory learning (the enhancement of visual acuity and contrast sensitivity of the open eye after monocular deprivation, or MD, in which vision in one eye is blocked) and ocular dominance, or OD, plasticity (a shift in the ocular dominance of neurons in the binocular part of the visual cortex toward the open eye after MD). (Scale bar, 500 μm.) (D) The higher magnification image of the lesion border (region demarcated by the black rectangle in C shows the intact tissue and cortical layering in the perilesional zone. The left brain hemisphere is illustrated showing that the lesion was restricted to the cortex without affecting the underlying white matter or subcortical regions. (C) Nissl-stained frontal section through a lesion center 7 d after lesion induction. We overlaid the scheme with an optically recorded retinotopic map from the binocular part of V1 to directly illustrate the spatial relationship of the PT-lesion and V1. (Scale bar, 1 mm.) (B) Scheme illustrating average lesion location and size: lesion center was located in the left primary somatosensory cortex (S1), on average 1.3 mm anterior to (the anterior border of) the primary visual cortex (V1) and 1.8 mm lateral to the midline. (A) Top view of a mouse brain with a PT-lesion in the left hemisphere (red dotted circle). Localization, size, and demarcation of the photothrombotic (PT) lesion in the mouse cortex.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
